Proof-of-concept code has been released after researchers disclosed a maximum severity remote code execution vulnerability in Erlang/OTP SSH. Successful exploitation could allow for complete takeover of affected devices.
Background
On April 16, Fabian Bäumer, Marcus Brinkmann, Marcel Maehren, and Jörg Schwenk of the Ruhr University Bochum in Germany disclosed a critical vulnerability in Erlang/OTP SSH to the OpenWall vulnerability mailing list. Additionally an official advisory was posted to the GitHub project for Erlang/OTP crediting the researchers for their disclosure.
| CVE | Description | CVSSv3 | VPR |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2025-32433 | Erlang/OTP SSH Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 10.0 | 10 |
*Please note: Tenable’s Vulnerability Priority Rating (VPR) scores are calculated nightly. This blog post was published on April 18 and reflects VPR at that time.
Analysis
CVE-2025-32433 is a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting the Erlang/OTP SSH server. The vulnerability exists due to a flaw in the SSH protocol message handling which could allow an unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code. According to the advisory, all users running Erlang/OTP SSH servers are impacted and to assume impact if your application utilizes the Erlang/OTP SSH library. This vulnerability received the maximum CVSSv3 score of 10.0 and when the SSH daemon is running as root, allows an attacker to completely compromise an affected device. At the time this blog was published, no known exploitation has been observed, however with the ease of exploitation and critical severity, we anticipate attacks will occur soon.
Proof of concept
On April 17, researchers at Platform Security released a public proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for CVE-2025-32433. The writeup notes that the PoC was generated with the help of ChatGPT and Cursor, and that it was fairly simple to do so using those AI tools. The PoC initiates an SSH protocol negotiation as a normal client would. But, before authenticating the user, the client sends an unexpected message with an arbitrary command. The vulnerable server will process these messages and execute the commands. A patched server will disconnect immediately upon seeing these messages prior to authentication. An additional PoC has been released, and the Horizon3 Attack Team posted on X (formerly Twitter) that they had developed a PoC but have chosen not to release it as of writing.
Just finished reproducing CVE-2025-32433 and putting together a quick PoC exploit, surprisingly easy. Wouldn’t be shocked if public PoCs start dropping soon. If you’re tracking this, now’s the time to take action. #Erlang #SSH pic.twitter.com/hBqJMfFHMN, Horizon3 Attack Team (@Horizon3Attack) April 17, 2025
Solution
Erlang/OTP has released patches to address this vulnerability.
Affected Versions Fixed Versions OTP-27.3.2 and below OTP-27.3.3 OTP-26.2.5.10 and below OTP-26.2.5.11 OTP-25.3.2.19 and below OTP-25.3.2.20 If immediate patching cannot be performed, restricting access via a firewall or disabling the SSH server are mitigation steps provided by Erlang/OTP. However, we strongly recommend upgrading as soon as possible to fully remediate this vulnerability.
Identifying affected systems
A list of Tenable plugins for this vulnerability can be found on the individual CVE page for CVE-2025-32433 as they’re released. This link will display all available plugins for this vulnerability, including upcoming plugins in our Plugins Pipeline. Additionally, customers can utilize Tenable Attack Surface Management to identify hosts running Erlang/OTP SSH Server.
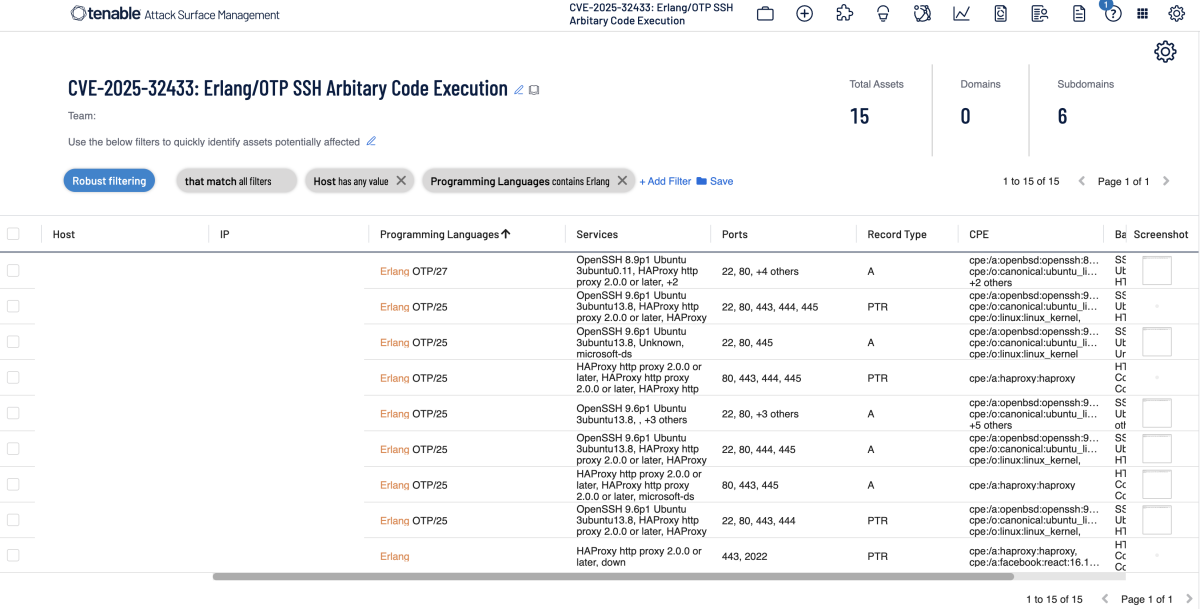
Get more information
Openwall mailing list announcement for CVE-2025-32433 Advisory for CVE-2025-32433 Join Tenable’s Security Response Team on the Tenable Community. Learn more about Tenable One, the Exposure Management Platform for the modern attack surface.

First seen on securityboulevard.com
Jump to article: securityboulevard.com/2025/04/cve-2025-32433-erlang-otp-ssh-unauthenticated-remote-code-execution-vulnerability/
![]()

